Introduction
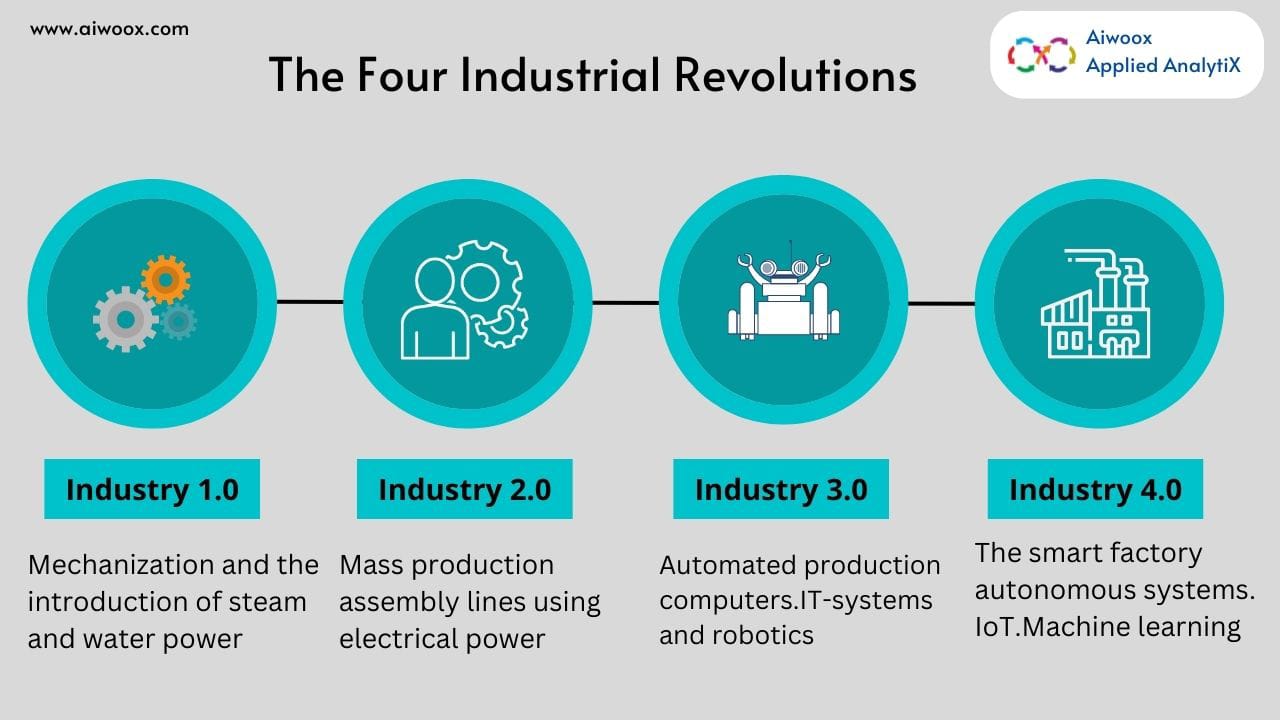
The impact of AI in manufacturing is game-changing. Many different industries are benefiting from artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), and the manufacturing sector is about to undergo a significant transformation. Manufacturing sector, which includes the production of automobiles, machinery, pharmaceuticals, food & beverages, paint & coatings, and much more, is a massive business that employs about 13 million of people in US, In order to increase workforce productivity and overall production speed, manufacturing organizations are continuously looking for ways to lower labor costs and minimize downtime. AI/ML can help with both of these challenges. AI and ML in the manufacturing sector are solving these problems and providing opportunities. Following image shows the four industrial revolutions in manufacturing industry.
In the modern world, data is a priceless resource. The fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0, is taking place in manufacturing, and businesses are placing a lot of emphasis on real-time data processing, artificial intelligence software, automation, and device interoperability. Manufacturers are modifying data to produce at faster, more effective rates by utilizing important innovations like internet connectivity hardware and machine learning. These technologies are intricate, though, and their effective implementation requires knowledge of a wide range of computer science and industrial topics.
What is ML/AI?
In everyday slang, the terms ML and AI are frequently used together. In this article, we’ll also combine these terms. Although they are interrelated, they are also a bit different from one another. Deep learning is a word that is related to both of these concepts.
The three terms are so related to one another in the following ways: Deep learning, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are collectively referred to as DLMLAI. And the fundamental idea behind this technology is to teach machines how to think by giving them data so they can identify patterns and make decisions on their own.
By giving machines cognitive capacities, AI/ML technology in manufacturing generally tries to automate complex or repetitive industrial tasks. Identifying patterns in industrial processes or workflows gives machines cognitive abilities or intelligence. This is achieved by first gathering enough data and then analyzing it to find the patterns that are of use.
Read more about Machine learning- Click Here
ML AI use cases in Manufacturing Industry
1. Smart Manufacturing: Robots with artificial intelligence (AI) are used in smart manufacturing, which eliminates the need for repetitive programming. Additionally, because they are robots, they can complete repetitive jobs without complaint and don’t require a break (or a long break) from their work. In contrast to humans, they are also less prone to error, according to a Industry analysis that claims collaborative and context-aware robots can increase productivity by up to 20% in labor-intensive environments.In order to do important manufacturing tasks like welding, painting, drilling, die casting, etc., self-learning robots can be developed.Fanuc, a Japanese automation company, and BMW Group are two examples of businesses that employ smart manufacturing techniques inside their facilities.
2. Predictive maintenance(PdM): With the use of sensors that measure variables like vibration, temperature, magnetic flux etc., rotating machinery is monitored using the current maintenance technique known as predictive maintenance. The health of your assets is then assessed or shown on your cloud platform, which is accessible online from any location in the world.
The way AI/ML technology assists in this situation is by assisting in the early determination of the acceptable or healthy limits of the machine parameters.
Your PdM system can also receive the healthy limits manually by testing the unit over time. Naturally, this will require time and work. The ISO 10816 vibration severity chart is one example of a standard chart that is used to determine permitted limits. However, the problem in this instance is that every machine has its own limitations, and these conventional charts only give an approximation. Therefore, all of these roadblocks can be removed by your PdM system, which is built on AI/ML technology.
3. AI/ML in Logistics and SCM: In order to prevent workplace injuries, the use of AI/ML in logistics and SCM involves creating self-learning smart robots that can simplify challenging activities like moving large products or lifting objects, as well as finding a solution to the problem of over stacking or under stocking of goods.Additionally, semi-automatic or completely automatic trucks are becoming more common. According to research by Acumen Research and Consulting, their market share will reach $88 billion USD by 2027.
In order to increase the efficiency of the supply chain and the safety of both people and products, this technology has advanced beyond trucks and now includes self-driving ships. Additionally, Rolls Royce, a manufacturer of luxury automobiles, is a current example of this. They are using ML and image recognition in partnership with Google to power their ships for increased supply chain efficiency. According to statistics from Industry, AI-powered SCM can actually cut down on inventory overstocking by 20 to 50 percent, forecasting errors by 20 to 50 percent, and missed revenues by 65%.
4. Automation and robotics: Automation technologies powered by artificial intelligence are changing mass production across a range of industry sectors. Robots do routine, repetitive work, relieving staff from many responsibilities. According to a 2020 research, there were already 2,7 million robots used globally in manufacturing facilities in 2019. During the fourth industrial revolution, manufacturers updated their infrastructure to be competitive in their industries and keep up with the swiftly shifting market. Robots continue to drive the world’s industries, working alongside assembly lines, handling raw materials, welding, machining, packaging, and other duties. AI-powered robots offer new prospects for scalable work by enhancing operations quality, lowering the risk of downtime, operating around-the-clock, also in dangerous areas and challenging conditions.
Market forecasts suggest that there is still a strong demand for automation and robotics in the manufacturing sector, both for more traditional robots that perform simple, repetitive tasks and for the most advanced collaborative robots that are built to work safely along with a human workforce.
5. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): The other automotive giant, well-known for its variety of American cars, utilizes a different strategy for AI in its facilities. GANs are a subclass of machine learning techniques known as neural networks that may produce new images from collections of input images. GM is using GANs in generative design, on the border of artificial intelligence and additive manufacturing, with the goal of enhancing personalization, performance, and customization. GM uses software to analyze several design iterations and offer the best options based on the requirements and constraints (such as materials, money, etc.) of the developed components. GANs provide new opportunities in an industry that previously relied on conventional techniques like injection molds when combined with 3D printing. In a day when there is an increasing desire for customization and the creation of unique items, shapes and combinations that were previously impossible to manufacture could transform the automotive industry.
Probably not enough to convince decision-makers to use machine learning techniques is the demand for personalized cars. Given the bets placed on GANs and additive manufacturing to revolutionize the production of electric vehicles, there is a stronger demand for this approach.
6. Cyber security: The use of IoT technology by manufacturing businesses inside their facilities is a good thing, but it also makes them susceptible to cyber threats like hacking and phishing. According to current research, small businesses with yearly revenues under $5 million experience losses of about 13% of their overall revenue.
Cyber security solutions with AI capabilities are the answer to this issue. The advanced AI/ML system can accurately and automatically identify any cyber attack, stop it, and notify the security staff so they can take further action.
7. Customer Service: In order to fully satisfy a consumer, product creation goes beyond simply being sold to the customer. The best thing is that ML/AI algorithms can be used to this field as well.Smart AI applications created with the final product can assist by quickly understanding consumer problems and then offering better solutions for them. Additionally, the software can self-learn as a result of its cognitive capabilities, giving users a more customized experience over time.
8. Energy consumption forecasting: Finally, it is also possible to forecast energy consumption using ML/AI systems. With ML/AI, it is possible to create a predictive model that may predict future energy usage by collecting and evaluating data of various characteristics, such as temperature, lighting, and movement level within a building facility. This energy management achieved up to this level of efficiency will not only save energy costs but will also reduce GHG emissions.
9. Quality assurance processes: To increase productivity and quality control, the world’s largest manufacturer, BMW, which is based in Bavaria, uses AI in its manufacturing processes. The corporation collects significant amounts of data throughout the 30 hours it takes to construct an average automobile in the plant, which helps to enhance internal procedures. BMW has recently started laser-marking all metal sheets. Engraved codes allow algorithms to gather data on key parameters, making it simpler to track the manufacturing process and reducing the number of inspections that are required. Wear sensors are carried by the robots working on manufacturing lines, signaling when it is time to replace an electrode. This frees up workers from manually monitoring the status of electrodes. Other areas of the facility have sensors and algorithms that check for appropriate levels of dusting in the paint shop, monitor the accuracy of mounted components, and test the calibration of car keys; the last of these is a “homegrown” robot called Comfort Access.
10. Maximizing efficiency with predictive analytics: The multinational engineering and technology business Bosch plans to use artificial intelligence and machine learning to make its manufacturing facility green by 2023. The German-based company uses a software solution that combines data on electricity generation and consumption and has a preference for renewable energy sources. The system forecasts producing output and power requirements using AI/ML algorithms, which results in operation schedules for power consumption. Bosch is moving toward using renewable energy sources and buying green power, but the strategy wouldn’t work without achieving total sustainability, which is made possible by AI/ML technologies.
What Next ?
Contrary to common belief, human labor won’t likely be replaced by artificial intelligence; rather, it will complement and support it as we strive for Industry 4.0-inspired modern production. New positions will develop as older ones are replaced. For employees to have the abilities they need for the foreseeable future, experts recommend personnel ups killing and reskilling.
According to the World Economic Forum, the rapid advancement of technology could eliminate 85 million employment in the next years. The research also predicts that 97 million additional employment will be created throughout this time. The ability of robots and a retrained human labor to share work responsibilities, which, according to the WEF, may be divided equally by half, will be demonstrated over the coming years.
Conclusion
Automation, robots, and cutting-edge analytics have long played a significant role in the industrial sector. The widespread deployment of AI in manufacturing appears to be more of an industry evolution than a revolution. Technology has already here, and wider adoption is only a question of time. By 2025, smart factories will produce $37 trillion in revenue, claims z.